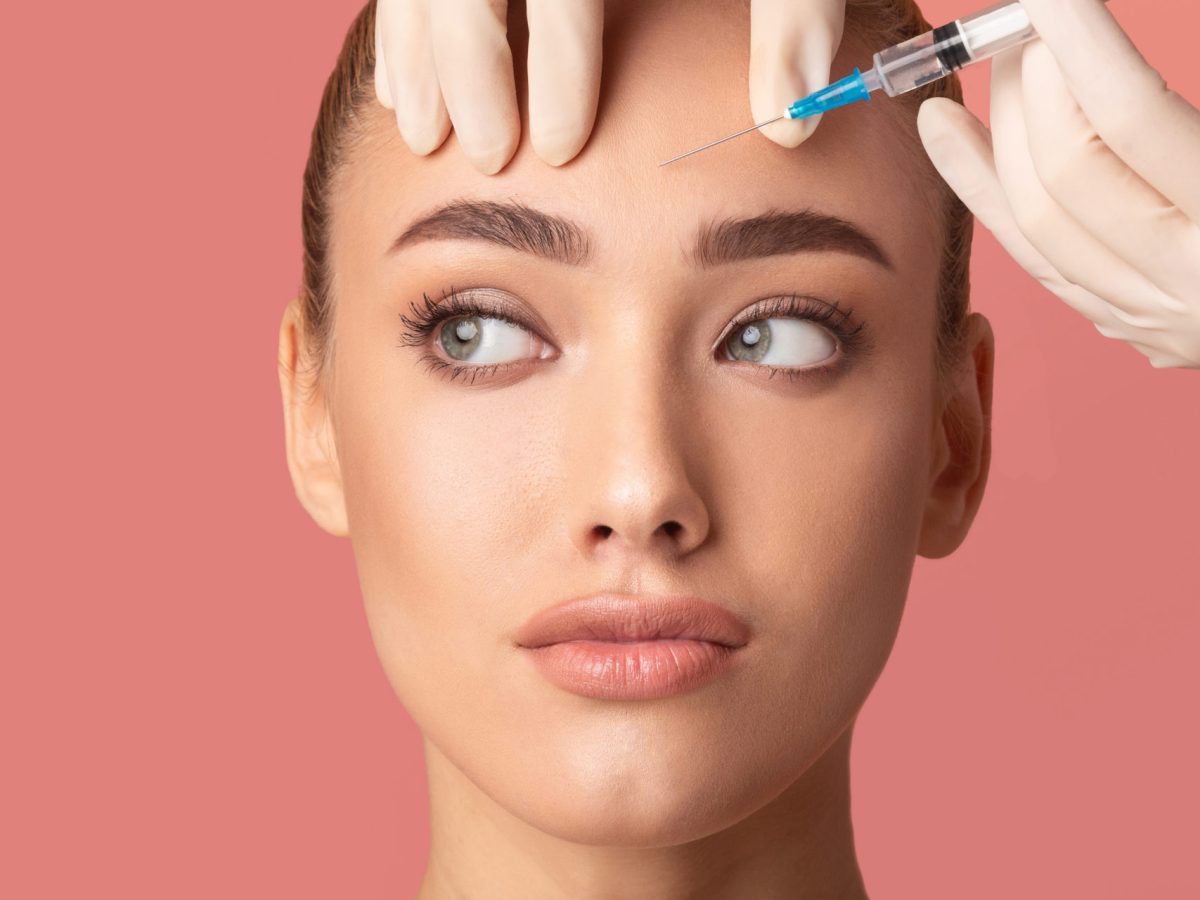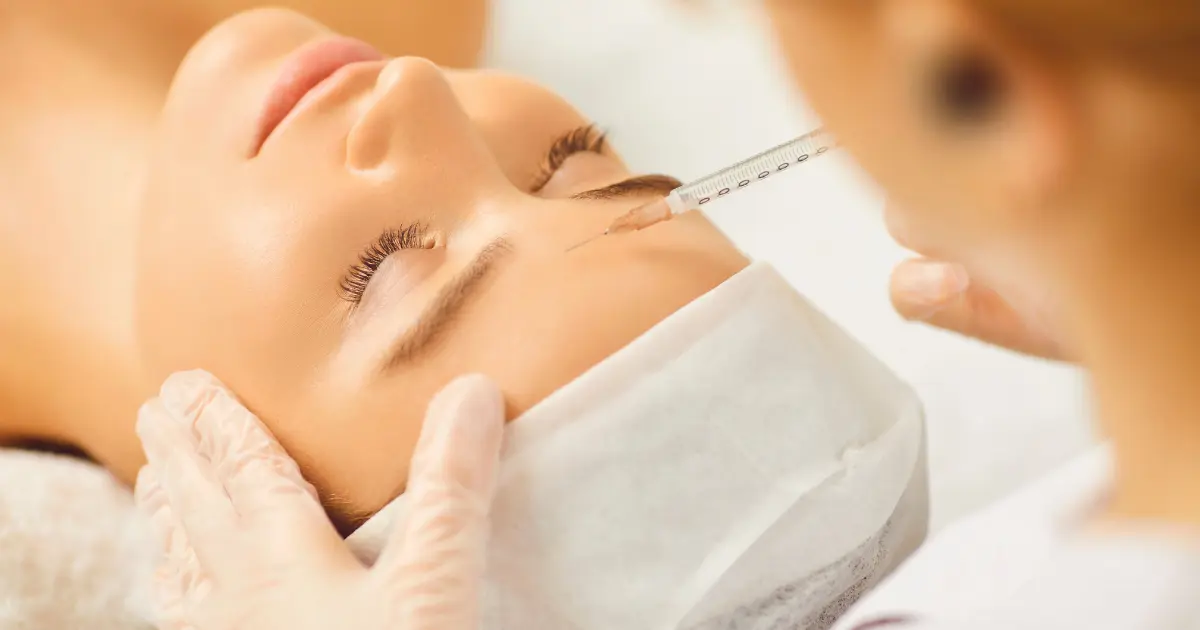
Botox is derived from the C. botulinum bacteria, which naturally occurs in various environments such as soil, lakes, forests, and in the intestinal tracts of mammals and fish. While these bacteria and their spores are typically harmless, they can produce Botulinum toxin, a potent neurotoxin, under certain conditions. This toxin is responsible for botulism, a serious illness.
In therapeutic contexts, Botox is used safely and with minimal side effects. It involves very small doses of Botulinum toxin, which temporarily paralyzes muscles and can benefit individuals with specific muscle or nerve disorders.
Botulinum toxin is available in several commercial forms, including:
People often refer to all these products as “Botox,” though Botox is a registered trademark.
Botox is a neurotoxin that disrupts nerve signaling processes that trigger muscle contraction. By preventing the release of acetylcholine, a chemical messenger, Botox stops muscle cells from contracting, resulting in temporary muscle paralysis. This helps reduce muscle stiffness and is particularly useful for various medical and cosmetic applications.
Botox is primarily known for reducing the appearance of facial wrinkles. It is the most popular cosmetic procedure in the U.S., with millions undergoing Botox treatments annually. Common treatment areas include:
The effects of Botox in these areas typically last between 3 to 12 months.
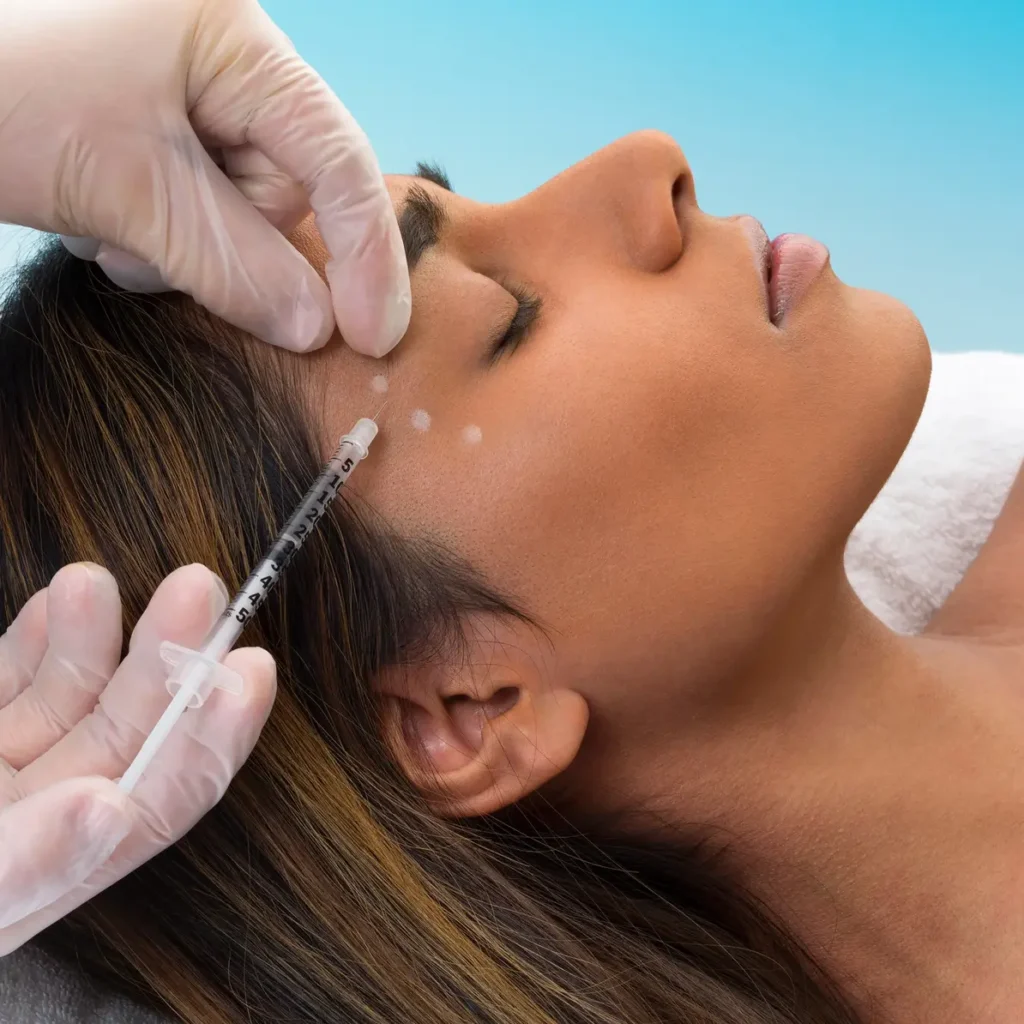
Botox is also used to treat several medical conditions, including:
Botox is sometimes used for off-label purposes, such as treating:
The Botox procedure involves diluting the toxin powder in saline and injecting it into neuromuscular tissue. The effects usually start within 24 to 72 hours and may last from 3 to 12 months.
The cost of Botox varies based on its use (medical or cosmetic), the provider, location, and number of units required. For cosmetic purposes, Botox treatments typically cost around $376 for areas like frown lines or crow’s feet. Results appear within 1 to 5 days and last for 4 to 6 months, with repeat treatments necessary to maintain results.
While generally well-tolerated, Botox can cause side effects such as dry eye, upset stomach, numbness, mild pain or bruising at the injection site, headaches, temporary eyelid drooping, or unwanted muscle weakness. More severe effects can include cardiovascular events or breathing difficulties in rare cases.
Botox, when administered by qualified professionals, offers a safe and effective way to address various cosmetic and medical concerns. For those considering Botox treatments, it’s essential to consult with a trained healthcare provider to ensure safety and effectiveness.
